Bike engine kits come in a variety of displacements (or “cc’s” as they’re commonly known) and with a wide range of mounting options. However, on the market are only two styles of engines: 2-strokes and 4-strokes. We’ve all heard the advantages and disadvantages to each, but have you ever wondered how it all works? Let’s check out the way each engine works:
2-stroke:

The reason these engines are called 2-stroke’s is because in order to power the engine there are only two strokes the engine performs: the compression stroke and the combustion stroke.
As fuel is pulled from the carburetor it is pressurized. As the piston travels down the cylinder a vacuum is created, opening the exhaust port and letting the pressurized fuel mixture into your cylinder.
The piston then travels up the cylinder to the spark plug. The spark plug gives off a spark that ignites the fuel and sends the piston back down the cylinder, opening the exhaust port. As the piston travels back up the cylinder some of the exhaust goes out of the exhaust port on the engine and new fuel is introduced into the cylinder.
4-stroke:
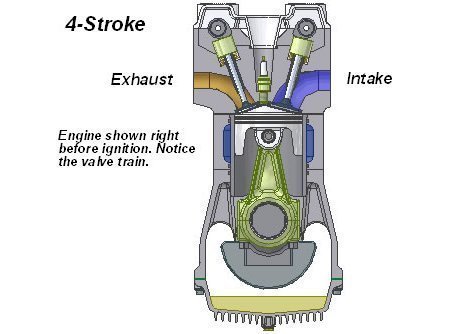
A big difference between the two styles of engines is that 4-strokes have intake and exhaust valves rather than ports for pulling in fuel and air. Also, the crankcase is separated from the chamber for combustion so you only need to pour oil into the oil reservoir to lubricate all bearings and gears. This is why there are 4 strokes needed to complete a piston cycle: intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion stroke, and power stroke.
The first stroke opens the intake valve. The piston travels down the cylinder, pulling the fuel and air mixture from the carburetor. This stroke is known as the intake stroke.
Then the piston travels up the cylinder, closing the intake valve. Right before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC) the spark plug gives off a spark to ignite the fuel mixture. The piston’s journey to the top of the piston this is known as the compression stroke.
After the fuel ignites it will force the piston back down the cylinder. This stroke is the one that gives the engine its power, also known as the power stroke.
When the piston is forced down, the exhaust valve is opened. The piston then travels back up the cylinder and as it does, the exhaust gases are emitted through the exhaust port. The piston will move up the cylinder and begin the process all over again.
You can see from both that there is a compression and combustion stroke.
However, 4-strokes have a combustion stroke every other piston revolution, whereas the 2-stroke combusts the fuel mixture every rotation.2-strokes do not have valves and fire every piston revolution, making them faster than 4-strokes. On the downside, 2-strokes have less parts they are not as reinforced as 4-stroke. Moreover, not adding the correct oil/fuel mixture will lock up and virtually ruin the entire engine.
Because 4-strokes have valves and a separate crankcase for oil, the engine will perform very well and last alot longer than 2-strokes. On the flip side, 4-strokes are generally heavier and slower so they will be more for commuting rather than racing. There are advantages and disadvantages to both, but gaining a better understanding of how a certain engine operates will help your decision between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke bike engine kit.
 The reason these engines are called 2-stroke’s is because in order to power the engine there are only two strokes the engine performs: the compression stroke and the combustion stroke.
As fuel is pulled from the carburetor it is pressurized. As the piston travels down the cylinder a vacuum is created, opening the exhaust port and letting the pressurized fuel mixture into your cylinder.
The piston then travels up the cylinder to the spark plug. The spark plug gives off a spark that ignites the fuel and sends the piston back down the cylinder, opening the exhaust port. As the piston travels back up the cylinder some of the exhaust goes out of the exhaust port on the engine and new fuel is introduced into the cylinder.
The reason these engines are called 2-stroke’s is because in order to power the engine there are only two strokes the engine performs: the compression stroke and the combustion stroke.
As fuel is pulled from the carburetor it is pressurized. As the piston travels down the cylinder a vacuum is created, opening the exhaust port and letting the pressurized fuel mixture into your cylinder.
The piston then travels up the cylinder to the spark plug. The spark plug gives off a spark that ignites the fuel and sends the piston back down the cylinder, opening the exhaust port. As the piston travels back up the cylinder some of the exhaust goes out of the exhaust port on the engine and new fuel is introduced into the cylinder.
 A big difference between the two styles of engines is that 4-strokes have intake and exhaust valves rather than ports for pulling in fuel and air. Also, the crankcase is separated from the chamber for combustion so you only need to pour oil into the oil reservoir to lubricate all bearings and gears. This is why there are 4 strokes needed to complete a piston cycle: intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion stroke, and power stroke.
The first stroke opens the intake valve. The piston travels down the cylinder, pulling the fuel and air mixture from the carburetor. This stroke is known as the intake stroke.
Then the piston travels up the cylinder, closing the intake valve. Right before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC) the spark plug gives off a spark to ignite the fuel mixture. The piston’s journey to the top of the piston this is known as the compression stroke.
After the fuel ignites it will force the piston back down the cylinder. This stroke is the one that gives the engine its power, also known as the power stroke.
When the piston is forced down, the exhaust valve is opened. The piston then travels back up the cylinder and as it does, the exhaust gases are emitted through the exhaust port. The piston will move up the cylinder and begin the process all over again.
You can see from both that there is a compression and combustion stroke.
However, 4-strokes have a combustion stroke every other piston revolution, whereas the 2-stroke combusts the fuel mixture every rotation.2-strokes do not have valves and fire every piston revolution, making them faster than 4-strokes. On the downside, 2-strokes have less parts they are not as reinforced as 4-stroke. Moreover, not adding the correct oil/fuel mixture will lock up and virtually ruin the entire engine.
Because 4-strokes have valves and a separate crankcase for oil, the engine will perform very well and last alot longer than 2-strokes. On the flip side, 4-strokes are generally heavier and slower so they will be more for commuting rather than racing. There are advantages and disadvantages to both, but gaining a better understanding of how a certain engine operates will help your decision between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke bike engine kit.
A big difference between the two styles of engines is that 4-strokes have intake and exhaust valves rather than ports for pulling in fuel and air. Also, the crankcase is separated from the chamber for combustion so you only need to pour oil into the oil reservoir to lubricate all bearings and gears. This is why there are 4 strokes needed to complete a piston cycle: intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion stroke, and power stroke.
The first stroke opens the intake valve. The piston travels down the cylinder, pulling the fuel and air mixture from the carburetor. This stroke is known as the intake stroke.
Then the piston travels up the cylinder, closing the intake valve. Right before the piston reaches top dead center (TDC) the spark plug gives off a spark to ignite the fuel mixture. The piston’s journey to the top of the piston this is known as the compression stroke.
After the fuel ignites it will force the piston back down the cylinder. This stroke is the one that gives the engine its power, also known as the power stroke.
When the piston is forced down, the exhaust valve is opened. The piston then travels back up the cylinder and as it does, the exhaust gases are emitted through the exhaust port. The piston will move up the cylinder and begin the process all over again.
You can see from both that there is a compression and combustion stroke.
However, 4-strokes have a combustion stroke every other piston revolution, whereas the 2-stroke combusts the fuel mixture every rotation.2-strokes do not have valves and fire every piston revolution, making them faster than 4-strokes. On the downside, 2-strokes have less parts they are not as reinforced as 4-stroke. Moreover, not adding the correct oil/fuel mixture will lock up and virtually ruin the entire engine.
Because 4-strokes have valves and a separate crankcase for oil, the engine will perform very well and last alot longer than 2-strokes. On the flip side, 4-strokes are generally heavier and slower so they will be more for commuting rather than racing. There are advantages and disadvantages to both, but gaining a better understanding of how a certain engine operates will help your decision between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke bike engine kit.




3 comments
dibya ranjan sahoo
Nice
Owais lodhi
Thank you for the knowledge.
Rip Daniels
Thanks was very good information.